EnterpriseLibrary version- 5.0
Download url
Language used in code sample below - C#
Logging is a very important feature for many applications and serves the very critical purpose in a software application's life. Logging enables to look for monitoring data and also document what is happening in-side and out-side of the application; also known as auditing.
Most common
places to log such activities, information and data are:
1- Flat files (.log/.txt)
2- Event logs (Windows event viewer) and
3- Database.
In the absence of logging application block, the logging code needs to be repeated in the application at many places. This code will also include .NET library and function calls based on type of place you want to log the information. Hence,
logging application block simply de-couples the logging functionality from the application code.
Configuring the Logging Application Block
1- Open your Visual Studio project, if not already available, add an app.config file
2- Open Microsoft Enterprise Library console.
3- In the Blocks menu, choose "Add Logging Settings" option, this will appear as shown here:
4- Based on your requirements add listners (File, Event, Database etc.).

5- Describe "Event Log" target listner
6- Describe "Flat File" trace listner
 7- Describe "Message Formatter"
7- Describe "Message Formatter"
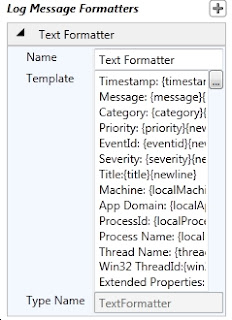
Now save this configuraton by clicking File--> Save option. and choose your added .config file,
this will be modified and will appear as shown here.
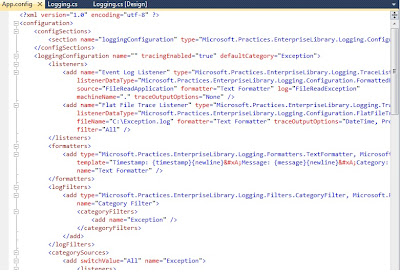
Now you can add the code to enable the Logging from your application into the defined "Target Trace Listners" in our case "Flat File" and "Event Log".
I have designed a Windows Form application which reads a file, from provided path location, if file is found it loads the cntent into the text box, else in case of an exception "FileNotFoundException" the error info is logged into the Log file (c:\exception.log) and Event Log.

C# Code will look like this
using Microsoft.Practices.EnterpriseLibrary.Logging;
private void
btnReadFile_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
StreamReader sr = null;
try
{
sr = new StreamReader(txtFilePath.Text);
txtFileContent.Text = sr.ReadToEnd();
}
catch (FileNotFoundException)
{
txtFileContent.Text="Exception details
logged log file
and Event Viewer";
LogEntry objLog = new LogEntry();
objLog.Message = "Please provide valid
Filename";
objLog.Categories.Add("File Read
Error");
Logger.Write(objLog);
}
finally
{
if (sr != null)
{
sr.Close();
}
}
}
Now if you open the C:\Exception.log you will see:
----------------------------------------
Timestamp: 10/1/2012 7:35:03 PM
Message: There is no explicit mapping for the categories 'File Read Error'. The log entry was:
Timestamp: 10/1/2012 7:35:03 PM
Message: Please provide valid Filename
Category: File Read Error
Priority: -1
EventId: 0
Severity: Information
Title:
Machine: VIDYAVRAT-PC
App Domain: LoggingApplicationBlock.vshost.exe
ProcessId: 9164
Process Name: C:\VidyaVrat\Microsoft .NET\Application Code POCs\EnterpriseLibrary-Application Blocks\LoggingApplicationBlock\LoggingApplicationBlock\bin\Debug\LoggingApplicationBlock.vshost.exe
Thread Name:
Win32 ThreadId:13588
Extended Properties:
Category:
Priority: -1
EventId: 6352
Severity: Error
Title:
Machine: VIDYAVRAT-PC
App Domain: LoggingApplicationBlock.vshost.exe
ProcessId: 9164
Process Name: C:\VidyaVrat\Microsoft .NET\Application Code POCs\EnterpriseLibrary-Application Blocks\LoggingApplicationBlock\LoggingApplicationBlock\bin\Debug\LoggingApplicationBlock.vshost.exe
Thread Name:
Win32 ThreadId:13588
Extended Properties:
----------------------------------------
Also, if you open the EventVwr.exe then you will see:
This concludes that how Logging application block enables you to write small amount of code to do such a critical task of auditing.

















